Overview
This section walks you through setting up the Mapp Engage React Native integration from scratch, covering essential installation steps and initial configuration settings for both iOS and Android. By the end of this section, your app will be equipped with Mapp's engagement tools, ready to handle push notifications, in-app messages, and location-based targeting.
Procedure
Step 1: Ensure Prerequisites are Installed
Before starting, confirm that the following tools are installed:
Node.js: Required for running JavaScript code on your system. Download Node.js if not already installed.
Yarn: Used for dependency management. Download Yarn and follow their installation instructions.
CocoaPods (iOS only): Required for managing iOS dependencies. Download CocoaPods.
Supported Platforms:
OS: iOS 10+ (requires Xcode for development).
Android: Android 21+ (Lollipop).
React Native Versions:
"react": "18.2.0""react-native": "0.73.4"
Mapp React Native plugin:
The React Native plugin is supported by the Mapp SDK (iOS SDK 6.0.2+ / Android 6.0.13+).
Step 2: Install the Mapp React Native Plugin
Run one of the following commands in your project directory to install the Mapp plugin, enabling your app to access Mapp’s engagement features:
npm install https://www.npmjs.com/package/react-native-mapp-plugin --save
# Or alternatively, use Yarn:
yarn add react-native-mapp-pluginThis adds the Mapp plugin to your dependencies, allowing your app to access Mapp’s engagement features.
Step 3: Platform-Specific Configuration
Follow the steps below based on your target platform.
For Android
Add the Google Services plugin to
build.gradle:apply plugin: 'com.google.gms.google-services'Set Permissions (if using Geolocation): Add the following permissions to
AndroidManifest.xml:<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_BACKGROUND_LOCATION" />
For iOS
Install CocoaPods: Run the following command from the iOS directory to install dependencies:
cd ios && pod installEnable Capabilities: Push Notifications and Background Modes for Remote Notifications and Location Updates.
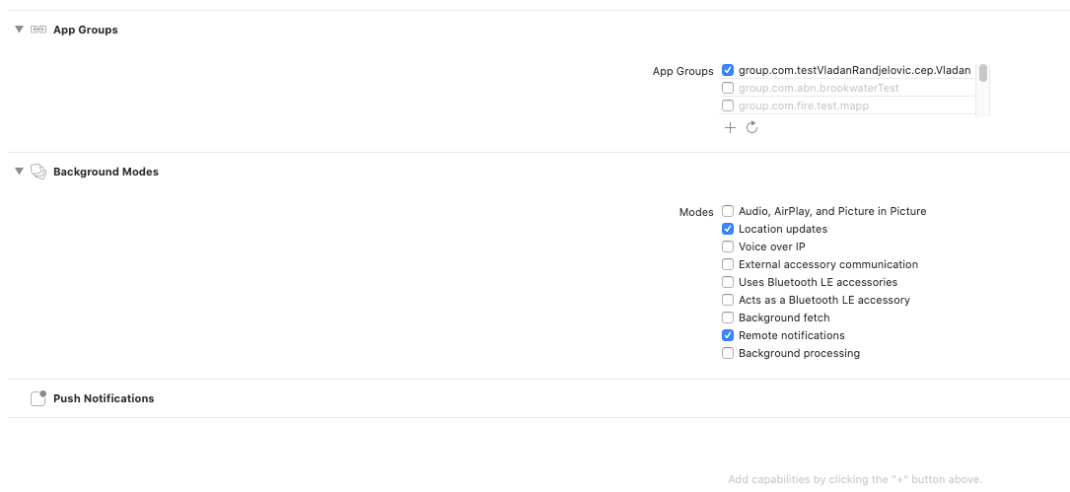
Create Configuration File: Create an
AppoxeeConfig.plistfile and include it in the application target:.png)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd"> <plist version="1.0"> <dict> <key>inapp</key> <dict> <key>custom_fields</key> <array> <string>customString</string> <string>customNumber</string> <string>customDate</string> </array> <key>media_timeout</key> <integer>5</integer> </dict> <key>sdk</key> <dict> <key>app_id</key> <string>your app id</string> <key>dmc_system_id</key> <integer>your dmc id</integer> <key>sdk_key</key> <string>your sdk key</string> <key>is_eu</key> <true/> <key>open_landing_page_inside_app</key> <false/> <key>jamie_url</key> <string>your inapp server url</string> <key>apx_open_url_internal</key> <string>YES</string> </dict> </dict> </plist>
With these steps complete, your app is ready for deeper configuration. Continue to the Bridge API Guide to enable features like push notification handling, in-app messaging, and custom event tracking.