1 Introduction
The Visitors Preference scope allows you to identify users who show a repeated interest in specific content — not just one-time interactions.
Instead of simply checking whether an event occurred, preference filters evaluate how frequently certain behaviors happen over time. This enables a deeper understanding of user affinities and supports more precise segmentation.
2 How to Set It Up
To use a preference filter in Mapp Intelligence:
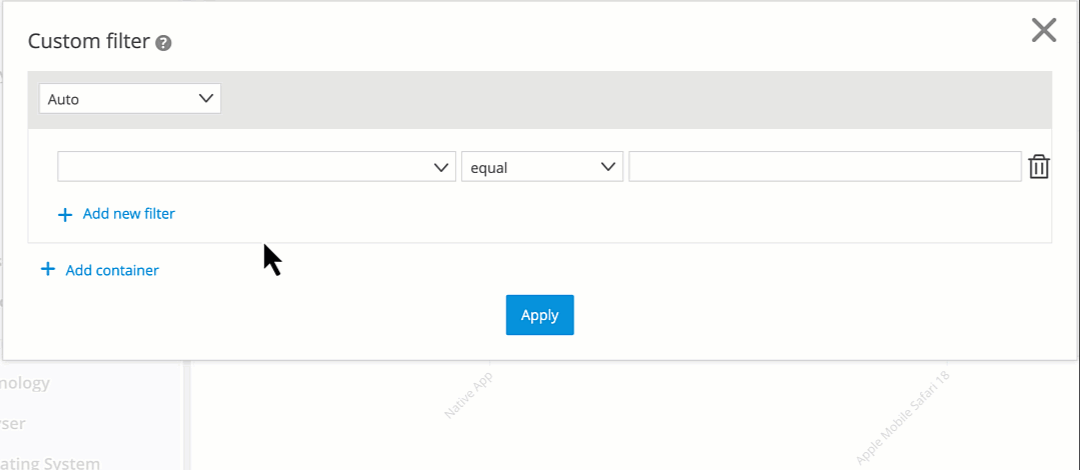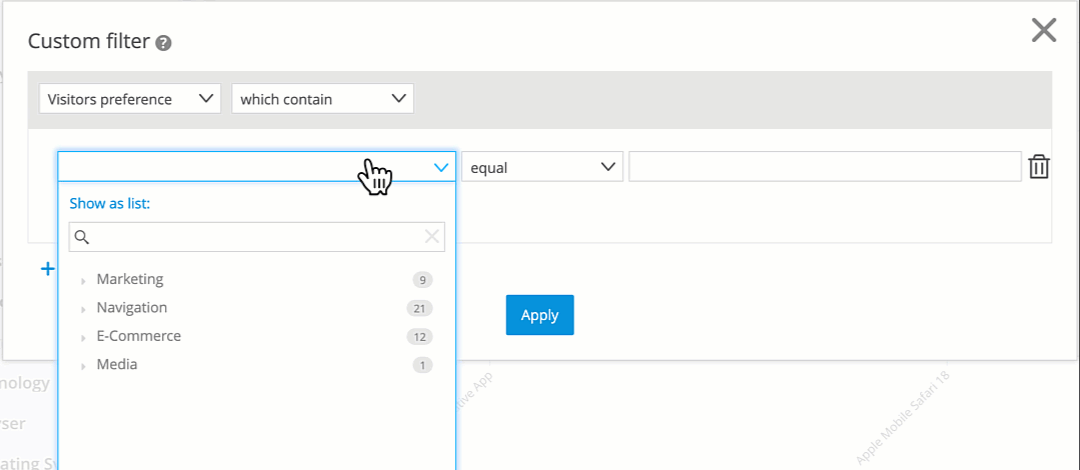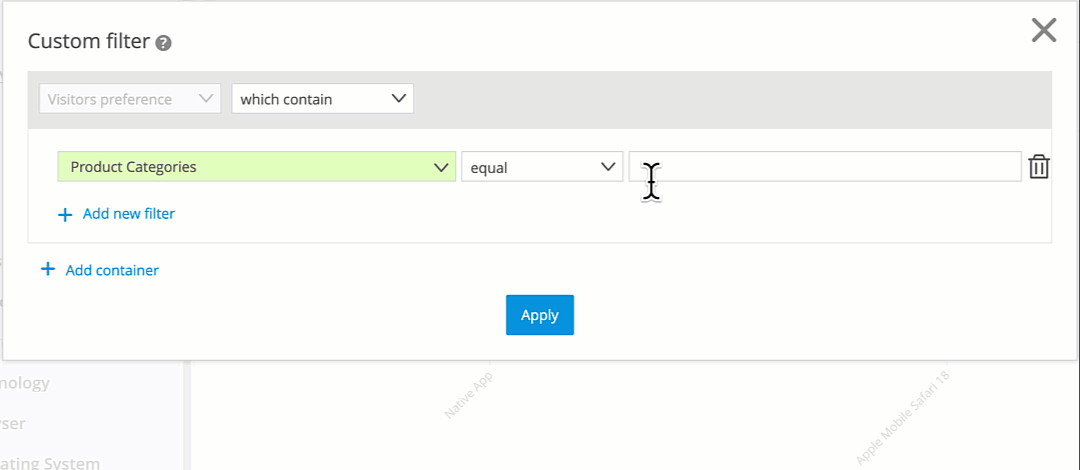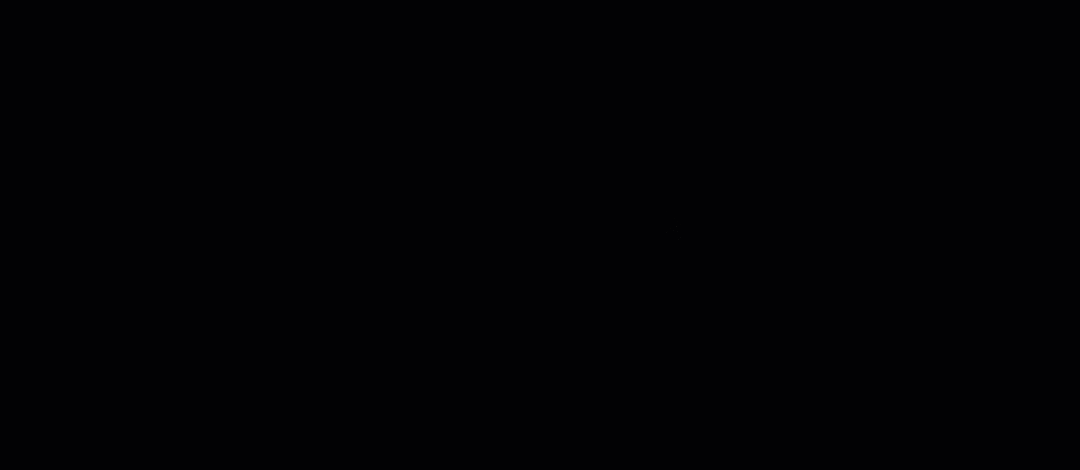
Create a new filter.
Select Visitors Preference as the scope.
Choose a dimension that is available for this scope (see table below).
Example: Preference Filter for Running Shoes
Not all dimensions are supported — only those that represent repeatable user interactions. The available list is shown in the next section.
3 Supported Dimensions (by Classification)
The following dimensions are supported by the Visitors Preference scope. They are grouped by classification:
Classification | Supported Dimensions |
|---|---|
Pages | Pages, Content Groups, Page Parameters |
Marketing | Campaigns, Campaign Categories, Campaign Parameters |
E-Commerce | Viewed Products, Viewed Product Categories, E-Commerce Parameters |
Media | Media, Media Categories |
4 Rules for Combining Filters
When using the Visitors Preference scope, certain restrictions apply to how filters can be combined:
Within a single container:
All selected dimensions must share the same standard scope.
Example: Pages and Marketing can be used together (Page scope), but not Pages and E-Commerce.
Across multiple containers:
You can use more than one container with the Visitors Preference scope, but containers must be combined using AND.
5 How Interest Is Calculated
Whether a user is considered interested is determined by one of two rules. The system applies the logic automatically, based on the selected dimension. Each classification uses a specific metric as the basis for evaluation:
Classification | Metric used |
|---|---|
Pages | Page Impressions |
Marketing | Campaign Clicks |
E-Commerce | Viewed Products |
Media | Media Views |
Rule A: Frequency and Share
A visitor is considered interested if:
The event occurred more than once, and
It accounts for more than 20% of all relevant events by that visitor
Example:
A visitor generated 100 Page Impressions in total. Of those, 60 were from the Content Group Sport.
→ Since the value exceeds 20%, Rule A is fulfilled.
Rule B: Dominance within a set of values
Alternatively, a preference is recognized if:
Events from at least two different categories occurred, and
One value occurred more frequently than the average of all other values in the same dimension
Example:
A visitor triggered Page Impressions in the following Content Groups:
Sport: 40
News: 20
Travel: 10
→ Average of other Content Groups = (20 + 10) / 2 = 15
→ Sport (40) > 15 → Rule B is fulfilled
You don’t need to configure or calculate anything manually — Mapp Intelligence applies the logic in the background.
6 Use Case Examples
Here are three practical ways to use preference filters in your daily work:
Identify content affinities for better targeting
Segment users who regularly consume content from specific content groups. For example, users who frequently access sections such as Sustainability, Health or Travel.
Personalize product experiences
Use product-related preference filters to show tailored offers. For example, visitors with a high interest in running shoes, outdoor gear or specific brands.
Optimize campaign messaging
Target users who have clicked on specific types of campaigns multiple times. For example, users who often click on promotional banners or newsletter campaigns can be addressed with tailored visuals or messaging frequency.