Rules in Tag Integration allow you to control the execution of plugins or scripts based on specific conditions. This ensures that your tracking logic is precise, efficient, and tailored to your website or app’s behavior.
1 What Are Rules?
Rules define the circumstances under which a plugin or script should execute. They allow you to restrict actions to specific pages, user interactions, or any custom-defined conditions. This flexibility ensures that your tracking implementation aligns with your business logic.
2 Types of Conditions for Rules
Rules in Tag Integration can be created based on three main types of conditions:
Parameters
Parameters are predefined variables that have been configured in the parameter section of Tag Integration. These can include:
JavaScript variables: Values extracted directly from the webpage’s DOM or script execution.
Mobile parameters: Variables specific to mobile app tracking, such as device type or app session data.
Example: You have a parameter named product_name, which is sent whenever a product’s information is displayed.
Rule: If the parameter product_name is present, classify the page as a product page.
Use Case: This rule ensures that specific tracking, such as measuring user interactions with product details, is only executed on product pages.
URL
Rules can be based on the page’s URL, including support for static conditions and Regular Expressions (RegEx) for dynamic patterns.
Example: URLs for product pages on your website contain the keyword product-view (e.g., https://example.com/product-view/item123).
Rule: If the URL contains product-view, the page is identified as a product page.
Use Case: Use this rule to load tracking scripts only on product pages, improving efficiency and avoiding unnecessary script execution on other pages.
Events
Event-based rules trigger actions when specific user interactions occur. These interactions can include:
Clicks (e.g., on a button or link).
Mouseover (hovering over an element).
Form submissions (e.g., submitting a registration form).
Custom events (e.g., a unique JavaScript function or behavior).
Example: On your e-commerce site, users click an “Add to Basket” button. This button doesn’t reload the page but calls a JavaScript function in the background.
Rule: When the “Add to Basket” button is clicked, log the interaction as a tracking event.
Event type: Click
Element: The button identified by its ID or class (e.g., id="add-to-basket")
Use Case: Track all “Add to Basket” events without needing a page reload.
3 Example Event-based rule “Add to basket”
In the following example, there is a simple button on the website:
<button type="button" id="test">Click here</button>Once a visitor clicks this button, the message "Button clicked" is issued.
To define a rule and integrate the function example as mentioned above, proceed as follows:
In Tag Integration, navigate to Rules in the main navigation.
Click New rule to add a new rule.
Now specify the new rule as follows:
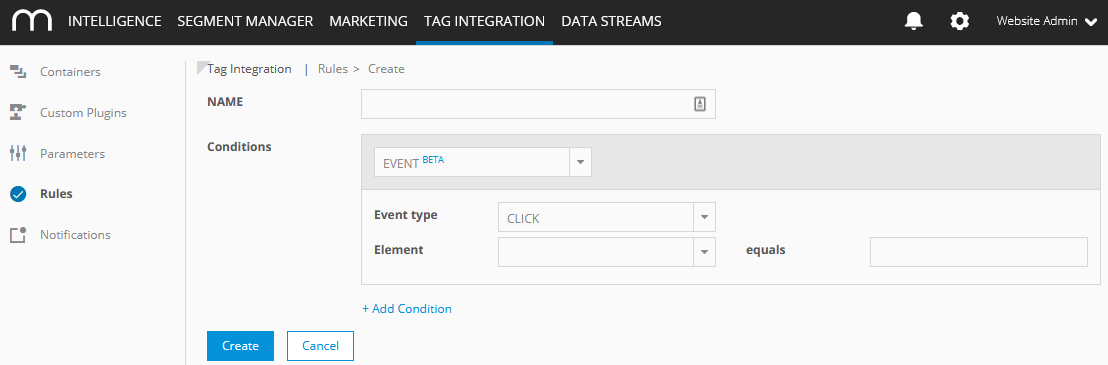
Parameter
Description
Example
Name
Enter the name of the new rule.
Button clicked
Conditions
Select from the dropdown list the condition.
Click "Add condition" if you want to define further conditions.
Event
Event type
Choose the event type from the dropdown list:
click
mouse over
form
custom event
Click
Element
Choose from the dropdown list the required element:
ID
class
and then enter the element value in the provided text field.
ID
Finally, click Create to save your settings. The new rule will be added to the list of all existing rules in the overview.
Create now a custom plugin, which will call the JavaScript alert(); function. Navigate to Custom Plugins in the main navigation area.
Click New plugin to add a new custom plugin.
Now specify the new custom plugin as follows:
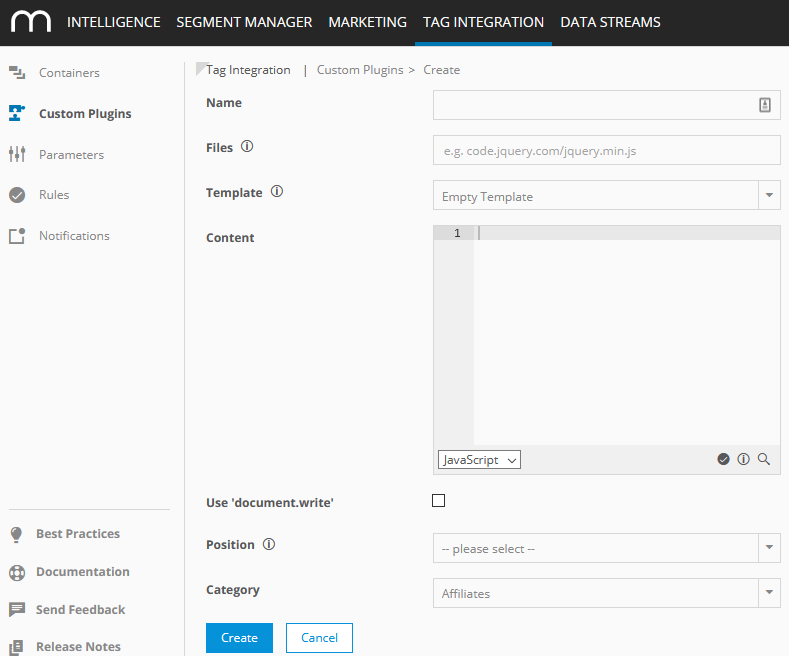
Parameter
Description
Example
Name
Enter the name of the new custom plugin.
Button clicked
Files
You can specify URLs to external JavaScript files, which are necessary for the execution of this plugin.
Template
From the dropdown list, choose a template to use as the script.
Content
Add the JavaScript function, which should be executed by this plugin.
Custom plugins allow the execution of arbitrary JavaScript code. Parameters that are created in Tag Integration based on JavaScript variables or URL-parameters can be used here. The following function can then access parameters:ti_parameter("Name of the created parameter");alert("Button clicked);
Use 'document.write'
"Document.write" is a JavaScript method to add content dynamically to an HTML document. If you are using tags with this method, activate this option to prevent that the browser overwrites the existing document and replaces it with the content of the "document.write" call.
Position
Specify where the script should be loaded:
head
After <BODY>
Before </BODY>
instantly
instantly
Category
From the dropdown list, select the category.
WebAnalysis
Click Create to save your settings. The new custom plugin will be added to the list of all existing custom plugins in the overview.
Now you can add the newly created plugin to the appropriate container.
Finally, assign the rule created in step 3.