Configuration options enable precise control over which campaigns are considered for attribution and how they are weighted.
1 Overview of the Attribution Configuration Process
Configuring attribution models in Mapp Intelligence involves several key steps, summarized in the flowchart below. The process begins with defining website goals, selecting a default attribution model, and optionally configuring alternative models. You then define the scope of attribution (internal, external, or both), choose relevant data sources, and select the metrics to be calculated.
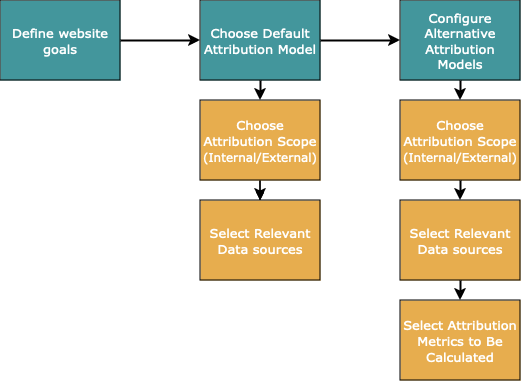
Detailed explanations for each step and term are provided in the sections below.
2 Default Attribution Configuration and Alternative Models
The default attribution model is defined in the Marketing Configuration and applies to all website goals unless an alternative model is specified.
Key Rules for Default Attribution:
Supported Models: Only models where a single campaign can “win” are supported.
Default Setting: The last campaign wins by default, considering only external campaigns.
This configuration provides a simple attribution setup, focusing on the final external interaction before a website goal is achieved.
Alternative Attribution Models
For more tailored analysis, alternative attribution models can be defined for each website goal. These models allow you to explore multiple perspectives on your campaign performance simultaneously..png)
Parallel Usage of Alternative Models:
By assigning different metrics to each alternative model, you can analyze your data from various angles. For example:
Use the default model to focus on last-touch attribution for quick insights.
Set up an alternative model to evaluate the overall impact of multiple campaigns using a multiple-assignment model.
Compare the results side-by-side to gain deeper insights into your campaign strategy.
Configuration:
Alternative models are configured under Mapp Q3 > Configuration > Goal, enabling goal-specific calculation settings to suit various campaign strategies..png)
Edit the attribution the change essential settings.
.png)
With alternative models, marketers can access diverse views of the same data set, ensuring more informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Learn more about attribution models here:
3 Relevant Data Sources
Every campaign in your attribution model is tied to a specific data source. Data sources define how campaigns and user actions are tracked and determine which interactions are eligible for attribution.
3.1 Primary and Secondary Data Sources
Primary Data Sources
These are essential for tracking campaign interactions and are always active. You cannot deselect primary data sources. They include:
URL Parameters (Media Codes): Campaign identifiers, such as utm_source or custom parameters.
Page Names: Specific web pages tied to campaign performance.
Events: User actions, such as clicks or form submissions.
Primary data sources provide the foundation for campaign tracking and are automatically included in attribution calculations.
Secondary Data Sources
These add flexibility to your attribution model, allowing you to include or exclude additional campaign types. You can configure which secondary sources to include:
SEO: Organic search campaigns.
Other Sources: Includes uncategorized referrers or unknown sources.
Social Media Sources: Non-paid social interactions.
Direct Entry: Visits where users enter your site directly without a referral source.
If a secondary data source is excluded, associated campaigns will not contribute to attribution, and no value will be assigned to them.
.png)
3.2 Configuring Data Sources
To customize your attribution model:
Include Relevant Secondary Sources: Ensure campaigns critical to your strategy, such as SEO or social media, are included as data sources.
Exclude Irrelevant Sources: For cleaner analysis, omit sources that don’t align with your goals, such as direct entries if they are not part of your campaign strategy.
Lern more about data sources in this article: Setting up Campaigns.
4 Attribution Scope (Internal/External)
The internal/external campaign flag allows you to distinguish between campaigns originating from your website or app (internal) and those driving traffic to your site from external sources (external). This separation is critical for maintaining accurate attribution logic and ensuring meaningful analysis.
4.1 Internal Campaigns
Internal campaigns track interactions within your owned channels, such as:
Teasers or banners displayed on your website.
Dynamic elements like carousels, pop-ups, or promotional links within your app.
In-app campaigns to drive engagement or conversions.
Internal campaigns are ideal for analyzing how your on-site or in-app elements contribute to achieving website goals. For example, you might use an internal campaign to measure how a homepage banner influences product purchases.
4.2 External Campaigns
External campaigns track all traffic sources driving users to your site, such as:
Emails
Referrers
Affiliates
SEO/SEA campaigns
Social media ads
External campaigns provide insights into the performance of outbound marketing efforts and partnerships, helping you evaluate how these channels contribute to conversions.
4.3 Why Separate Internal and External Campaigns?
Combining internal and external campaigns into a single Customer Journey often leads to skewed attribution statistics. This happens because:
External campaigns typically aim to bring traffic to your site, while internal campaigns focus on navigating traffic already on your site.
Including both in one Customer Journey can make it unclear which campaign type deserves credit for achieving a goal.
To maintain clean and actionable data, we strongly recommend creating separate attribution models for internal and external campaigns.
4.4 Setting Up Internal and External Campaigns
Attribution Settings:
When configuring an attribution model, you can decide whether to calculate attribution for:
Only External Campaigns: Focus on acquisition campaigns.
Only Internal Campaigns: Analyze on-site engagement.
All Campaigns: Include both internal and external campaigns in the same Customer Journey.
.png)
Campaign Settings:
For every individual campaign, you can define whether it is an internal or external campaign.This designation is made in the campaign’s settings and determines how the campaign is classified during attribution calculations.
.png)
5 Attribution Metrics
Metrics define the measurable outcomes tracked within your attribution models, such as revenue, order value, or specific user actions. By configuring metrics, you decide which data points are available for analysis within the attribution logic of a selected model.
5.1 How Metrics Work with Attribution Models
Default Attribution Model
For the default model, all e-commerce metrics you use in combination with campaigns are automatically calculated based on the default attribution logic.
These metrics require no additional configuration and are available automatically.
Alternative Attribution Models
For alternative attribution models, you must explicitly choose which metrics should be calculated and available for analysis.
Selected metrics are then created with detailed names to provide insights into their specific settings. These names help you understand the exact attribution logic applied when analyzing data in the frontend.
Single Assignment Models
Single-assignment models (where one campaign is credited) allow multiple metrics to be calculated simultaneously within the same model.
.png)
Multiple Assignment Models
For multiple-assignment models (e.g., Data-Driven Attribution with Shapley Values), only one metric can be calculated per model. If you need to analyze multiple metrics, you must set up separate models for each.
5.2 Available Metrics
Default e-Commerce Metrics:
Standard metrics included by default, such as:
Order Value
Qty Orders
Conversion rate
Custom e-Commerce Parameters:
Metrics tailored to specific business needs, such as:
Parameters with shopping cart reference (e.g., “Several Values” configuration).
User-defined event-based metrics, like newsletter sign-ups or file downloads.
Metric Naming Convention
Metrics follow a standardized naming format to ensure clarity:
[Name of the attributed metric] ([Attribution Type], [Internal/External]), [Website Goal]Example: Order Value (Attribution multiple, external), Order
.png)
6 Best Practices for Configuring Metrics
Activate Only What You Need:
Select only the essential metrics for your analysis to keep your list manageable.
Plan Ahead:
Metrics cannot be retroactively activated. Data collection begins only after you save the configuration, so review requirements carefully before saving.
Use Metric Names Effectively:
Detailed metric names help you understand the logic applied, especially when working with multiple attribution models.
Separate Metrics for Multiple Assignment Models:
Since only one metric can be calculated per multiple assignment model, configure separate models for each metric you want to analyze.